By Prof. Caroline Wamala Larsson
Imagine a farmer in rural Uganda who cannot make a mobile payment to their local agrovet because the village has no reliable coverage. Or a college student in Zimbabwe locked out of online classes because data costs consume too much of her family’s income. These are not isolated stories; they are daily realities for millions of Africans.
Connectivity is the backbone of economic growth, social inclusion, and civic participation. Yet nearly three-quarters of Africans remain offline or under-connected. Telecom regulators shape the environment where digital innovation can thrive. By setting fair rules and fostering competition, they create the conditions for affordable, reliable access that benefits all. They are key enablers of a vibrant digital ecosystem.


One initiative making this support tangible is the ICT Policy & Regulation – Institutional Strengthening (iPRIS) programme, coordinated by SPIDER in partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR). iPRIS offers regulators a year-long cycle of technical training, project management coaching, and peer-to-peer exchanges across Africa and Europe. iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa”
Since its launch in November 2023, iPRIS has engaged regulators from more than 30 countries, alongside regional bodies: ARTAC, CRASA, WATRA, EACO. Each cohort develops practical projects aligned with national priorities, which often evolve into regulatory reforms.
The impact is already visible. In Tanzania, regulators pioneered Direct-to-Mobile Satellite Guidelines, extending connectivity to remote areas. In Mozambique, a Change Initiative grew into a national roaming regulation that allows rural families to remain connected even when one network fails. In Mauritius, regulators are safeguarding the digital ecosystem with new Cybersecurity Guidelines, strengthening trust in online platforms and preparing for a 5G-driven future. Uganda has stepped onto the global stage by hosting the ITU Global Symposium for Regulators (GSR 2024), bringing 900 delegates to Kampala and demonstrating Sub-Saharan Africa’s leadership in digital governance.
These milestones are the result of collaborative efforts across governments, regulators, development partners, and regional bodies. iPRIS is proud to have contributed as part of this wider community driving digital transformation.

At WATRA, a number of initiatives are ongoing, most of which have yielded results towards providing meaningful connectivity in the sub-region, and some of these initiatives include;
WATRA is also proud to play an active role in the achievement of the Digital Transformation Strategy (DTS) 2020 – 2030 for Africa towards ensuring meaningful connectivity across all levels in the continent from the first to the last mile. Through the iPRIS project as well, various initiatives have been developed to promote connectivity across the sub-region, tackling critical areas of the telecommunications sector, ranging from Spectrum Management to 5G deployment. With other key collaborations with the ITU, Smart Africa, and other development partners, WATRA is making strides towards ensuring meaningful connectivity across West Africa and Africa at large.
For the regional regulatory organisations, inclusivity is not a slogan but a strategic goal. The 2023–2028 EACO strategic plan places bridging the digital divide at its core, bringing both urban and rural populations, women and men, into the digital economy. According to Nora Sitati, Liaison Manager at the East African Communications Organisation (EACO): “Diversity enriches innovation—men and women approach challenges differently, and when those perspectives converge, the solutions are stronger and more practical.”
Inclusivity, in this context, means ensuring that communities are not passive recipients of connectivity but active participants in shaping it.
This perspective underscores a crucial reality: data must guide action. Disaggregated statistics on gender, disability, or rural populations highlight who is excluded and why. Without such evidence, interventions risk being generic and ineffective. With data, telecom regulators, can tailor policies to expand access where it is most needed.
Inclusivity is also an economic imperative. Excluding women, youth, or rural communities not only perpetuates inequality, it denies economies the contributions of millions of potential digital consumers, workers, and innovators. In other words, empowering marginalised groups is both socially just and economically smart.
The obstacles to digital inclusion are deeply embedded in social structures—gender roles, class, age, and geography all shape access to resources and opportunities. Regulators cannot dismantle these barriers alone. Multi-stakeholder collaboration is essential, involving governments, telecom operators, academia, and civil society.
Awareness programmes and workshops are one way to bring multiple actors together. EACO, for example, has long demonstrated the value of including students and informal sector actors in its convenings. These efforts widen participation and help build solutions that reflect the needs of diverse communities.
Representation at the decision-making table is equally important. Solutions are more likely to succeed when the groups most affected—youth, women, persons with disabilities—are directly involved in shaping them. Exclusion at this stage only reinforces the very inequalities digitalisation seeks to overcome. Diversity is not just a matter of fairness; it is a driver of innovation. Different demographic groups bring unique perspectives to problem-solving. When rural and urban voices, men and women, young and old are all represented, regulatory frameworks and digital solutions become more practical, creative, and impactful.
The African Union’s Digital Transformation Strategy (2020–2030) recognises that Africa’s youth—nearly 60% of the population—are its greatest asset. Unlocking this demographic dividend requires lowering broadband costs, adopting gender-responsive policies, harmonising roaming regulations, and forging strong public–private partnerships to accelerate infrastructure rollout.
iPRIS is advancing this agenda by giving regulators the technical tools, data, and networks to deliver reforms that matter. Inclusivity, when embedded in regulation, ensures that Africa’s digital future is equitable as well as innovative.
As Doreen Bogdan-Martin, Secretary-General of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), reminded delegates at the Global Symposium for Regulators (GSR 2025) “Digital technologies – from AI to quantum – are advancing faster than any regulation can. The real race must not be to build the biggest or fastest systems, but to make these technologies work for everyone – especially while 2.6 billion people remain offline.”
Inclusive digital development is not simply about connecting people to the internet; it is about transforming lives, expanding opportunities, and empowering communities. By supporting regulators through programmes like iPRIS, and by embedding inclusivity into policy design, Africa can ensure that its digital revolution benefits all—especially those historically left behind.
As the continent moves toward 2030, regulators have an opportunity to align connectivity with broader goals of gender equality, social justice, and economic growth. This entails making deliberate efforts to close the digital gender gap, promoting affordable access for low-income households, and creating spaces where women, youth, and persons with disabilities can participate in shaping solutions.
If every regulatory framework places inclusivity at its core, Africa’s digital transformation will not only expand networks but also unlock the full potential of its people. The future is digital—and with inclusive regulation, it can also be equitable.
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and Institut luxembourgeois de régulation (ILR), as well as ARTAC, CRASA, EACO, and WATRA.
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
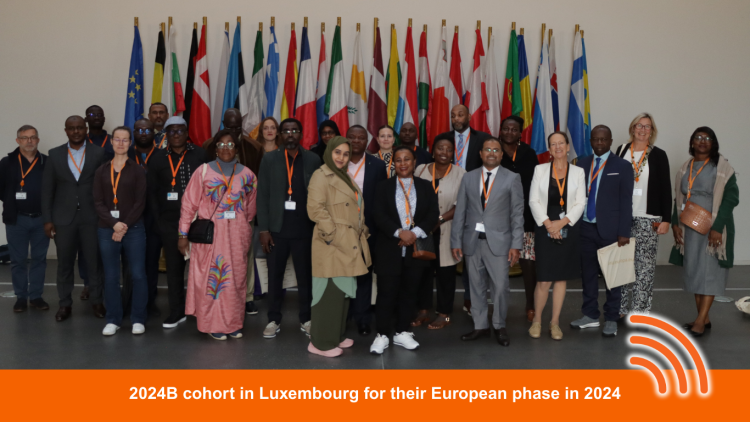
Luxembourg recently served as a crossroads for digital cooperation as telecom regulators from Africa and Europe convened for three weeks of intense peer-to-peer learning within the iPRIS Project. Participants included the National Telecom Authorities (NRAs) of Benin, Democratic Republic of Congo, Burundi, Cameroon, Gabon, Guinea, and Equatorial Guinea, as well as the Regional Regulatory Organisations (RROs) - ARTAO, EACO, ARTAC, and CRASA, and European partners (ARCEP France, BNetzA Germany, IBPT Belgium, and Deloitte). Against a backdrop of rapid digital growth, where affordability, inclusion, and security are pressing, this three-week programme was designed to foster cross-border cooperation and institutional capacity-building, alongside national Change Initiatives.
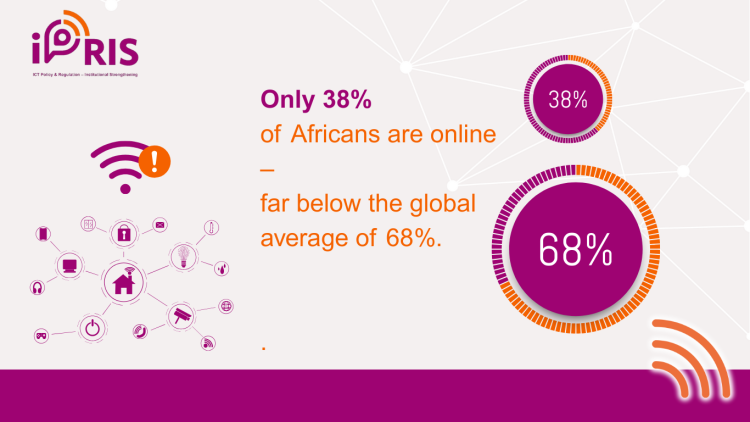
Despite Africa's digital boom, the latest ITU 2024 figures reveal a significant disparity between the continent and global averages, with 38% of the population online compared to 68% worldwide. While 85% of its population enjoys 3G coverage, the percentage falls to 60% for 4G and a mere 11% for 5G, indicating that infrastructure gaps have been present all along. It's more severe in rural areas, where one in four people are unable to connect to the Internet, and Internet penetration stands at 23% compared to 57% in urban areas. Another divide comes with gender disparities: while 43% of men are online, only 31% of women are, leaving millions of others, especially young girls, at risk of exclusion from the opportunities provided by the digital economy.
This is the sixth iPRIS cohort (2025C) organised by SPIDER, in collaboration with the Institut luxembourgeois de régulation (Luxembourg Regulatory Institute [ILR]). The sessions covered a wide range of themes, including institutional and legal frameworks, competition in a dynamic market, Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI), end-user protection, spectrum management, and cybersecurity.
The inaugural day set the tone for three weeks of joint work, grounding the participants in the principles of relevance, inclusivity, and sustainability of the iPRIS approach.
Welcoming the cohort, Luc Tapella, ILR Director, stressed, "initiatives for change must be relevant, inclusive and sustainable," and encouraged regulators to "embrace collaboration, peer-to-peer learning and openness as factors of lasting impacts." Jeanne Pietschmann, from the Luxembourg Ministry of Foreign Affairs, welcomed the participants and emphasised the strong cooperation between Luxembourg institutions and their African partners.

Caroline Wamala Larsson, SPIDER director, pointed out that "digitalisation is a global necessity, not only technically, but also socially and economically," thus framing connectivity as a development driver in all sectors. The afternoon's conclusion featured brief presentations of the Change Initiatives (CIs) being developed by each NRA. CIs are the cornerstone of iPRIS and are strategic projects undertaken to bridge the digital divide by addressing challenges and seizing opportunities in the ICT sector.

Another session during week 1 featured project management presented by Malena Liedholm-Ndounou, SPIDER expert. Project management is a key capacity that iPRIS is strengthening among NRAs to optimise their CIs. The session highlighted the effectiveness of SMART objectives in project management within the context of change initiatives: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.

Moreover, a discussion on spectrum management was led by Guy Mahowald, Head of the Frequency Department at ILR. For this session, ARCEP Benin's testimony on the subject of the various national regulations served as a relevant example. Faced with one of the major satellite service providers with a strong presence in sub-Saharan Africa, this Beninese regulator, a central player in the legal and technical reform of the ICT sector, has actively worked to build a sustainable and inclusive digital ecosystem, in particular by drawing inspiration from Nigeria's legislation, and has thus succeeded in supervising new providers in its market through regulation. This relevant testimony from Benin on the subject of regulation testifies to one of the pillars of the Joint European Offer.

The ICT experts also discussed Luxembourg's regulatory landscape, and ILR was described as a multisector autonomous regulator. Antoine Samba (ARCEP France) and Luc Birgen (ILR) brought perspectives on institutional and regulatory frameworks. Meanwhile, Julien Gilson (ARCEP France) and Annegret Groebel (BNetzA) detailed regulatory and competition models across Europe, examining independence through the clarity of mandates, transparency of procedures, and robustness of governance. Anael Bourrous (Deloitte) introduced the emerging regulatory challenges and the shifting balance of power among global platforms. In contrast, Chaïmae Baghdadi (ARCEP France) discussed the deployment of high-speed networks and the urgent matter of adapting certain provisions of the EU Digital Markets Act to African realities. These interactions highlighted the need to strike a proper balance between market oversight and operational autonomy, while reinforcing national capacities and ensuring that technology serves the interests of all, particularly in terms of gender equity, income-related access, and geographical distribution, thereby keeping technology in the hands of the people.

The second week involved more than just technical architectures; it also explored the societal and political underpinnings of digital regulations. Two themes were prominent on Monday morning in sessions led by experts from the SPIDER: Beyond Universal Access in Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) with Mr Cheikh Sadibou Sakho and Monitoring, Evaluation, Accountability, and Learning (MEAL) with Ms Katja Sarajeva.

Cheikh Sadibou Sakho highlighted the social dimensions of the digital divide, recalling that inclusion is not limited to infrastructure but also depends on social roles and gender. He highlighted the importance of embedding diversity, equity and inclusion, and introduced the notion of social construction of differences to guide regulators in developing their change initiatives (CIs). Katja Sarajeva, within the framework of MEAL, demonstrated how to place sustainable impact at the centre of actions through accountability, learning loops, and the use of disaggregated data, ensuring real and sustainable change.

On Tuesday morning, the focus was on a very interactive intervention on cybersecurity and regulation by Ms Asmaa Ouraini from the ILR. Later in the week, the sessions shifted to the strategic management of numbering and addressing, which were conducted by Tom Meyers (ILR) and Richard Klein (IBPT). They emphasised the need for long-term planning and coordination at a global level. With Sophie Steichen and Stefania Salvati (ILR), consumer protection sessions emphasised the importance of transparent contracts with clear indicators, as well as empowering users to utilise practical tools such as service comparers and quality monitors.



Representatives of four Regional Regulatory Organisations, who had been following the sessions via video conference, joined the delegates in person this week. They included Ms Bernice Edande (ARTAC), Mr Ruffus Samuel (ARTAO), Mr Alexis Sinarinzi (EACO) and Mr Trilok Dabeesing (ICTA/CRASA). Their simultaneous participation, a first, was a major step towards enhanced cooperation on a continental scale.

Alongside these discussions, site visits to SES and Luxembourg’s National Museum of Archaeology, History and Art highlighted the broader context of digital transformation, blending technical learning with cultural exchange and strengthening peer networks across Africa and Europe.

In the last week, everything from the 3-week course came full circle as participants aimed to flesh out the CIs that will present their plans to the NRA for the next year. The early sessions focused on addressing and numbering challenges in underserved rural areas, while also considering the broader issues of equity and resource allocation. The discussion on inclusive data and representation, led by Sadibou Sakho (SPIDER), underscored that analysis must be gender-disaggregated because dominant voices tend to mask the needs of women and other marginalised groups.
Working groups, in turn, applied these lessons to the CIs by strengthening governance structures, clarifying benchmarks, and adjusting international models to fit national realities. Expert feedback from SPIDER, ILR, and RROs further strengthened the teams' capacity-building proposals by identifying potential actors who could implement activities and proposing a timeline within which these activities logically fit.
The final moment of the round took place during the "Way Forward" sessions, during which the NRAs presented their project plans. The presentations demonstrated how each Change Initiative evolves from peer exchange, project management workshops, and diversity and inclusion sessions to deliver real regulatory change within the upcoming year.
Former iPRIS cohorts and ITP alumni joined this session remotely to provide comments and suggestions and to connect these new projects to ongoing reforms throughout Africa, further reinforcing iPRIS as a living collaboration network. The extremely rigorous feedback emphasised the importance of proper governance, communication, and adaptation to context, while also praising the cohort's ability to turn complex bottlenecks into concrete strategies.
The 2025C round ended with a sobering reminder that any regulation is both technical and socio-political. In a span of three weeks, the African and European telecom experts marched from the essentials of spectrum strategies into greater details on social imperatives of equity, accountability, and user protection, ultimately airing Change Initiatives that will firm up the reforms long after the peer exchanges.
The journey demonstrated that cross-continental collaboration is effective: European models provided benchmarks, while African realities introduced new perspectives on affordability, gender gaps, and rural connectivity. The peer learning process, significant feedback, and cultural exchange activities (field visits and informal discussions) helped forge the kind of trust necessary to take these ideas forward to action.
Watch highlights from this cohort's time in Luxembourg below
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and Institut luxembourgeois de régulation (ILR), as well as ARTAC, CRASA, EACO, and WATRA.
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
Luxembourg — 22nd September
As the iPRIS peer-to-peer training advances in Luxembourg, Week 2 focus shifted to the social, institutional, and protective aspects of digital regulation. Inclusion, accountability, cybersecurity, and consumer rights are explored during these sessions as founding principles of trustworthy digital ecosystems. The second Francophone cohort to participate in the iPRIS delved into these topics and more.
Read Week 1 highlights here
According to the GSMA Mobile Gender Gap Report 2025, in 2024, Sub-Saharan Africa was the only region to make headway in narrowing the mobile internet gender gap. The divide fell from 36% in 2022 to 32% in 2023, and further to 29% in 2024.
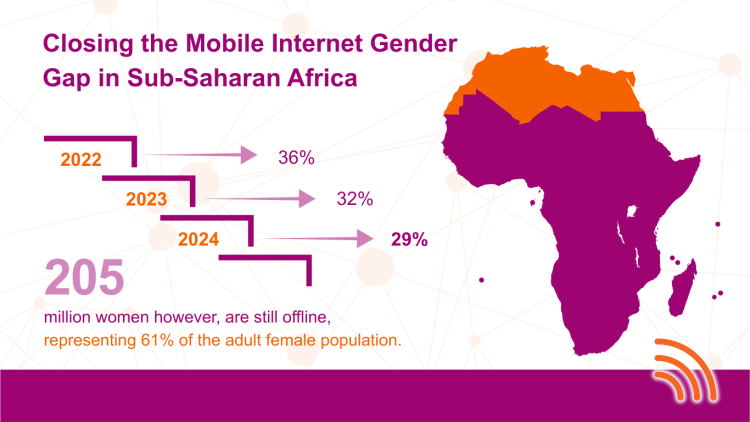
Yet, the challenge remains immense: about 205 million women in the region are still offline, representing 61% of the adult female population. These figures show a step in the right direction, but also highlight the need for appropriate regulation to bridge the digital divide, especially for women in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Various issues came up during the knowledge-exchange sessions in Luxembourg, currently shaping how regulators can foster trust and accountability in an ever-evolving digital environment:
Connectivity on its own does not guarantee equity. Unless purposely managed by regulators from a digital rights angle, such technologies reproduce gender, rural, and affordability barriers.
Monitoring and evaluation are not just about reports and checklists, but rather about ensuring that Change Initiatives trigger real-life change. When regulators monitor, adapt, and share lessons learned from them in the open, trust is created.
In an era marked by extreme digital connectivity, cybersecurity has become of utmost importance. According to UNDP, the second quarter of 2023 in Africa had the highest average weekly cyberattacks against any one organisation, approximating 2164 attacks. All individuals, including small businesses and large enterprises, are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Therefore, with ransomware, phishing, and fraud crossing borders, networks must be guarded to shield economies and societies.
Numbering and addressing are the invisible framework of communications, and consumer protection builds trust for digital services. Regulators must act with transparency, vigilance, and fairness in their dealings with these matters.
Institutional leadership and structured project management are key to transforming insights into lasting reforms. Success lies in moving from strategy to implementation.
Opening the week, Sadibou Sakho from SPIDER conducted a session on diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI). Connectivity, he reminded the participants, does not guarantee equity. Hence, he insisted that meaningful connectivity might become an empty phrase by emphasising that it needs to be reliable, affordable, and relevant.

The country reflections demonstrated the need to tackle affordability, urban planning, and gender disparities so that digital transformation can serve all citizens.
Katja Sarajeva from SPIDER walked participants through monitoring, evaluation, accountability, and learning (MEAL), asserting that regulation is deemed successful only if its impact outweighs the mere existence of documents.

She put equal importance on practical tools, stakeholder profiling, and continuous evolution in capturing lessons taught. She added that even small but practical outputs can contribute immensely to transformative long-term changes if aligned with an institution's priorities.
Asmaa Ouraini from Institut Luxembourgeois de Régulation (ILR) facilitated an extensive discussion on cybersecurity and network resilience, delving into how tiny cracks over time can turn into a roaring national crisis.

She stressed that the prime liability is often human error, hence awareness and digital hygiene should be positioned on par with technical defences. Pulling on the European NIS2 directive, Asmaa showed the merits of resilience through risk-based approaches and provided some examples as to how African regulators may tailor such frameworks within their own contexts.
Numbering and addressing sessions were steered by ILR's Tom Meyers and the Belgian Institute for Postal Services and Telecommunications (IBPT)'s Richard Klein.

They discussed how the allocation and portability of numbers affect interoperability and user choice and cited Belgium's blocking of fraudulent SMS messages as an example of consumer protection in practice.
Later in the week, Sophie Steichen and Stefania Salvati of ILR presented approaches to consumer protection, emphasising that trust in digital services depends on strong safeguards, from transparent operator obligations to active measures against fraud.
Malena Liedholm Ndounou of SPIDER returned to take the participants through the chapter on project management while reinforcing the idea of how SMART objectives and indicators are the two sides which turn the Change Initiative into concrete reform. The week closed with participant and ILR expert exchanges where national priorities were balanced against international best practices to ensure that each Change Initiative is context- and action-specific.

That week also extended itself beyond the freshly set training room. At SES, one of the world's leading satellite operators, the whole delegation received explanations on space-based connectivity for resilience and how it can be extended to underserved areas.

Cultural visits, including ones to museums and heritage sites, provided possibilities for exchange and reflection. These experiences made it clear that peer-to-peer learning is not just technical but also relational and cultural, thereby bridging the Atlantic between African and European regulators, beyond the formal bounds of this program.


Watch the highlights from Week 2 below and stay tuned for more updates on the remaining week of the peer-to-peer training sessions.
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and Institut luxembourgeois de régulation (ILR), as well as ARTAC, CRASA, EACO, and WATRA.
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
Luxembourg — 14th September
This September, Luxembourg stands at the center of digital cooperation, bringing together Francophone African and European telecom regulators for two and a half weeks of shared learning, strategic dialogue, and practical solutions to today’s connectivity challenges.
In an age where digital connectivity is the backbone of economic growth and social inclusion, bridging digital divides has never been more urgent. ITU estimates that approximately 5.5 billion people – or 68 per cent of the world’s population – are using the Internet in 2024. This represents an increase from only 53 per cent in 2019, with 1.3 billion people estimated to have come online during that period. However, this leaves 2.6 billion people still offline.
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER, in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and Institut luxembourgeois de régulation (Luxembourg Regulatory Institute [ILR]), as well as ARTAC, CRASA, EACO, and WATRA. It builds on the success of a similar programme implemented by SPIDER and PTS, which engaged 27 English-speaking African regulators between 2016 and 2022.
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).

This year’s Francophone cohort reflects the breadth and depth of regulatory experience across both continents. African National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs) participating include ARCEP Benin, ARCT Burundi, ART Cameroon, ARPTC Congo Kinshasa, ORTEL Equatorial Guinea, ARCEP Gabon, and ARPT Guinea. They are joined by Regional Regulatory Organisations (RROs) such as CRASA, WATRA, EACO, and ARTAC, alongside European peers including ARCEP France, BNetzA (Germany), IBPT (Belgium), and private-sector partner Deloitte.
The mix balances local realities with global perspectives, ensuring African regulators lead discussions while drawing on international expertise. Together, participants are charting a shared path towards stronger ICT regulation, fairer access, and a more connected future.

The 2025 peer to peer training round builds on the success of the 2024B Francophone cohort, which was the first French cohort from Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) to participate in iPRIS. This new cohort will continue iPRIS’s commitment to strengthening institutional leadership in ICT regulation and advancing affordable, inclusive, and sustainable digital transformation across Africa.

The iPRIS programme zeroes in on urgent priorities that define digital inclusion in Africa today:
These reflections underline the programme’s dual role: technical deep dive and cultural bridge-building.







Week 1 discussions were rooted in concrete national contexts. For example, in Equatorial Guinea, rural areas often rely on networks from neighbouring countries, with cross-border interference disrupting service quality. In Gabon, 90 per cent of the fibre market is controlled by a single operator, limiting competition and infrastructure sharing. Even when competition expands—as with the arrival of a third mobile operator in 2022—the market grew only 4 per cent, highlighting pressure on margins and the need for smarter regulation.
These examples illustrate why Change Initiatives (CIs) are central to iPRIS. Each telecom regulator during the 12-month training programme designs a CI aligned with their institutional priorities—whether infrastructure gaps, affordability barriers, or regulatory inefficiencies. Over the course of the 12-month session, CIs evolve from ideas into actionable project plans through two tracks: expert-led technical work (coordinated by ILR) and SPIDER-led coaching on project management.

One highlight of the week was a deep dive into spectrum management, facilitated by Guy Mahowald, the invisible yet indispensable resource that powers everyday life. This conversation addressed several spectrum topics across the session. One highlight was discussions around the challenges of balancing global standards with local realities, including the difficulties African regulators face with imported equipment, the publication of approved equipment lists, and the broader context of differing regulatory approaches between Africa and Europe.
Spectrum enables everything from mobile calls, texts, and internet access to Wi-Fi, GPS, satellite internet, Bluetooth devices, and even wireless microphones. Globally, spectrum governance is coordinated by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through its World Radiocommunication Conference. Regional bodies such as CEPT (Europe) and ATU (Africa) help align strategies, while national regulators like Luxembourg’s ILR develop detailed frequency plans and negotiate cross-border agreements.

The iPRIS peer-to-peer learning journey is designed to be both practical and transformative.
Facilitating the project management session, Ms. Malena Liedholm Ndounou of SPIDER emphasised that the real value lies in integrating those planning tools into actual outputs.
"Clear objectives and the right indicators help regulators see what's working and what's not. That's how Change Initiatives can drive down costs, close gender gaps, improve user experience, and build a more inclusive digital ecosystem," she stated.
Click the video below to view some moments from the first week
Since inception, iPRIS has engaged 31 national telecom regulators in Sub-Saharan countries, including Kenya, Nigeria, Ghana, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Eswatini, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo-Brazaville, Mauritania, Senegal, Togo, Lesotho, Mauritius, Rwanda, The Gambia, South Sudan, Liberia, Zimbabwe, Sierra Leone, Benin, Burundi, Cameroon, Congo-Kinshasa, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and Guinea-Conakry. Regional Regulatory Organisations (RROs)—CRASA, WATRA|ARTAO, EACO, ARTAC—play a central role in shaping the digital ecosystem.
Between 2023 and 2028, iPRIS will engage national and regional telecom regulators in 43 countries across sub-Saharan Africa to drive social and economic prosperity using ICT. Telecom regulators are key to ensuring ICT access, competition, consumer protection, and innovation to unlock development potential.
Stay tuned for more updates on the remaining weeks of the peer-to-peer training sessions.
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and Institut luxembourgeois de régulation (ILR), as well as ARTAC, CRASA, EACO, and WATRA.
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
From 6–24 September 2025, Luxembourg will host the second Francophone iPRIS round in Europe, bringing together telecom regulators and experts from across Francophone Africa for two and a half weeks of peer-to-peer learning, collaboration, and strategic action planning. The round builds on the success of the 2024B Francophone cohort, which was the first French cohort from Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) to participate in iPRIS. This new cohort will continue iPRIS’s commitment to strengthening institutional leadership in ICT regulation and advancing affordable, inclusive, and sustainable digital transformation across Africa.
Among the confirmed regulators are the National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs): ARCEP Benin, ARCT Burundi, ART Cameroon, ARPTC Congo Kinshasa, ORTEL Equatorial Guinea, ARCEP Gabon, ARPT Guinea, and, on the Regional Regulatory Organisations (RROs) side, WATRA, EACO, and ATRAC. They will also be joined by representatives from ARCEP France, BNETZA, IBPT, and Deloitte. This special mixture of institutions provides an environment that, from the learning perspective, allows a balance between local realities and international perspectives, an African-led space in partnership with global partners.
Africa has a lot of economic prospects in almost every field. The continent's young population is a huge opportunity in this digital age, which is why Africa needs to make digitally enabled socio-economic development a top priority. However, Africa remains the continent that is the least connected worldwide; only 38 percent of Africans were online as of 2024, as compared to 68 percent globally, according to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU, 2025).

These figures highlight the need for a shift in regulation and infrastructure growth in SSA. Access to affordable, reliable connectivity underpins economic competitiveness, social inclusion, and resilience. With such sectors being improved, the digital space in the continent has the potential to improve the lives of SSA’s population.
This round will focus on the ability of regulators to respond effectively to:
A key component of the iPRIS project is the planning and implementation of “Change Initiatives”, strategic projects designed to address specific challenges within each regulator's jurisdiction. Change Initiatives in earlier rounds have included:
The 2025 Francophone round will continue this approach, ensuring that knowledge exchange translates into measurable change at home. Following the Luxembourg workshop, a regional support team from the RROs will assist the regulators in implementing their change initiatives. The whole 2025C cohort will reconvene in one African country after 4 months to review progress and refine their projects. The effectiveness of the initiatives will be evaluated one year after the project’s commencement in 2026.
In addition to structured sessions, regulators will take part in field visits to operators, European regulatory institutions, and cultural landmarks. These experiences enrich the learning journey and provide space for informal collaboration.
iPRIS has engaged 24 national telecom regulators
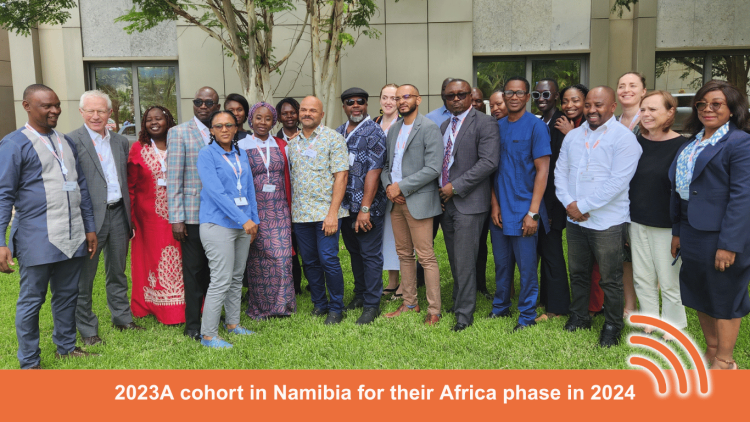
It has been an exciting journey built on information sharing and capacity-building. The first iPRIS cohort 2023A, comprising regulators from Nigeria, Kenya, Namibia, Eswatini, South Sudan, Zambia, and Sierra Leone, completed their iPRIS cycle in December 2024. They initially started their round in November 2023.

We also proudly welcomed the second iPRIS cohort (2024A) into the growing iPRIS alumni community. Their final wrap-up session in June marked the culmination of impactful Change Initiatives and strong regional collaboration. The 2024A cohort comprised South Africa’s ICASA, Lesotho’s LCA, Uganda’s UCC, Mauritius’s ICTA, The Gambia’s PURA, and Tanzania’s TCRA. The first-ever Francophone cohort comprised of NRAs representing the Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo Brazzaville, Mauritania, Senegal, and Togo.
So far, iPRIS has engaged 24 national telecom regulators in Sub-Saharan countries, including Kenya, Nigeria, Ghana, Namibia, South Africa, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, Eswatini, Central African Republic, Chad, Comoros, Congo-Brazaville, Mauritania, Senegal, Togo, Lesotho, Mauritius, Rwanda, The Gambia, South Sudan, Liberia, Zimbabwe, and Sierra Leone. Regional Regulatory Organisations (RROs)—CRASA, WATRA | ARTAO, EACO, ARTAC—play a central role in shaping the iPRIS ecosystem. From leading peer-learning sessions to offering guidance on cross-border spectrum harmonisation and NGSO frameworks, their contributions continue to drive the regional integration agenda.
Several iPRIS and predecessor programme cohorts have already translated Change Initiatives into regulatory milestones that are reshaping Africa’s digital landscape:
The Tanzania Communications Regulatory Authority (TCRA) has approved a pioneering set of Guidelines for the Provision of Direct-to-Mobile (D2D) Satellite Communication Services, making Tanzania one of the first African countries to establish a clear framework for satellite-enabled mobile connectivity.
This Change Initiative was designed and developed during the iPRIS 2024A cohort round by TCRA’s representatives – Eng. Aude Nishael Kileo, Ms. Gudila Proches Marick, and Mr. Christopher John Assenga.
With only 27% of Sub-Saharan Africa’s population using mobile internet by the end of 2023 (GSMA 2024), the Tanzanian framework positions the country at the forefront of regulatory innovation, ensuring satellite-to-device services can be safely and sustainably deployed to connect underserved and remote communities.
Download the official TCRA Guidelines

The Information and Communication Technologies Authority (ICTA) of Mauritius has launched comprehensive Cybersecurity Guidelines for all licensed telecom operators. These self-assessment tools help operators evaluate vulnerabilities, strengthen resilience, and prepare for the forthcoming 5G-driven digital ecosystem.
This Change Initiative emerged from ICTA’s participation in the iPRIS 2024A cohort, with the Mauritian delegation comprising Mr. Trilok Dabeesing, Ms. Priya Chutoorgoon, and Mr. Pralash Nahullah. Read More
Uganda’s Communications Commission (UCC) successfully hosted the Global Symposium for Regulators (GSR) 2024 in Kampala, demonstrating the country’s leadership in advancing inclusive ICT regulation. Read More
In Mozambique, a Change Initiative developed during the 2018B International Training Programme (ITP), the direct predecessor to iPRIS, has resulted in a landmark National Roaming Regulation.
The regulation was officially gazetted in 2025. It allows mobile subscribers in rural and underserved areas to access services from multiple operators, reducing coverage gaps and enhancing financial inclusion through mobile money services. Read More
These examples illustrate how iPRIS Change Initiatives are not only driving national reforms, but also informing regional harmonisation and shaping Africa’s contribution to global digital policy debates.
The African Union Digital Transformation Strategy (2020–2030) underscores that Africa’s youthful population structure is an enormous opportunity in the digital era. With the youth making up nearly 60% of Africa’s population, digital transformation must be at the centre of socio-economic development. Digitalisation is not just about connectivity. It is a driver of job creation, innovation, poverty reduction, and inclusive growth.
For regulators, the call to action is clear:
The second Francophone iPRIS round in Luxembourg is more than a peer-to-peer learning session. It is a strategic investment in Africa’s digital future. By equipping telecom regulators with knowledge, networks, and practical tools, iPRIS advances the vision of a continent where connectivity is affordable, inclusive, and transformative. The future of Africa is digital. Ensuring that it is also equitable and sustainable depends on the leadership strengthened through initiatives such as iPRIS.
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR).
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
The Tanzania Communications Regulatory Authority (TCRA) has now fully approved the usage of a groundbreaking set of Guidelines for the Provision of Direct-to-Mobile Phone Satellite Communication Services. These guidelines were developed directly from the National Regulatory Authority's (NRA) Change Initiative (CI), which was established during the iPRIS 2024A cohort round. The representatives of TCRA from the 2024A cohort are Mr. Aude Nishael Kileo, Ms. Gudila Proches Marick, and Mr. Christopher John Assenga.
Change Initiatives are strategic projects undertaken to bridge the digital divide by addressing challenges and opportunities within the ICT sector. They are the cornerstone of iPRIS and are specifically designed to align with the strategic agendas of regulatory bodies.
“We're happy to share that TCRA management has now approved these Guidelines, which will guide operators during the initial phase of deploying D2D services,” said Eng. Aude Nishael Kileo, one member of the TCRA 2024A team.
The Significance of the Guidelines
According to the GSMA Mobile Economy Sub‑Saharan Africa 2024 report, only 27% of the population in this region used mobile internet by end‑2023, while 60% of those in coverage remained unconnected due to affordability, safety issues, or skills gaps. With these Guidelines in place, Tanzania is well ahead in regulatory innovation in Africa, providing Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and Satellite Network Operators (SNOs) with a clear regulatory framework within which they can interact to deliver satellite-to-device (D2D) services.
The framework seeks to:
The Guidelines are the outcome of a broad stakeholder consultation, taking into account the views of MNOs, SNOs, and regional coordination priorities.
A Model Change Initiative
Within the iPRIS framework, CIs seek to improve NRA capacity by applying peer-to-peer learning. What TCRA achieved is an example of a targeted CI that, through peer dialogue, leadership engagement, and technical rigour, is translated into meaningful regulatory outcomes.
For further information, visit the TCRA website to access the official Guidelines for Provision of Direct-to-Mobile Phone Satellite Communication, or download the document directly here: https://www.tcra.go.tz/uploads/documents/en-1752839222-GUIDELINES%20FOR%20PROVISION%20OF%20DIRECT%20TO%20MOBILE%20PHONE%20SATELLITE%20COMMUNICATION.pdf
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR).
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
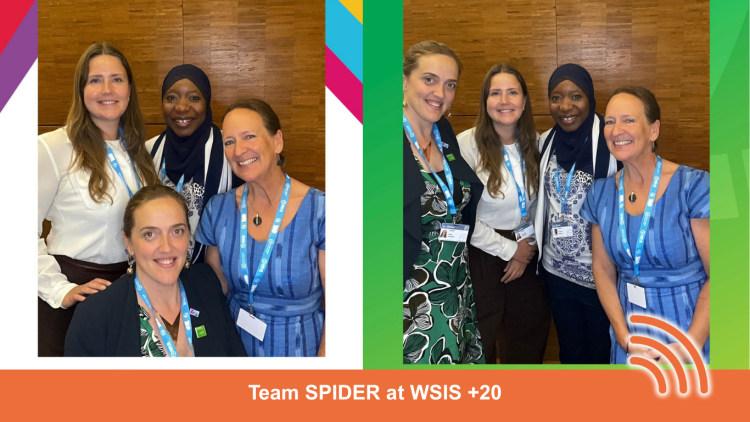
The global community gathered in Geneva from 7-11 July for a landmark moment in digital cooperation: the WSIS+20 Forum and AI for Good Global Summit 2025. These events aimed to foster deeper alignment between long-standing digital development goals and the rapid evolution of artificial intelligence.
Organised by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU), the two events were purposefully timed to celebrate 20 years since the launch of the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) while also ensuring that AI innovation advances in ways that support the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). WSIS+20 reviewed progress on building inclusive, rights-based digital societies, while AI for Good 2025 focused on human-centred, ethical AI solutions for global good.
The event featured participation from National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs) such as; Uganda Communications Commission, Posts and Telecommunications Regulatory Authority of Zimbabwe (POTRAZ), Ivory Coast - Telecommunications Regulatory Authority (ARTCI), Regulatory Authority for Posts and Telecommunications of Guinea (ARPT), Nigerian Communications Commission (NCC), and National Communications Authority (NCA), Somalia. Other notable participants include the Ghana Cyber Security Authority, African ICT Alliance (AfICTA), the Ministry of Posts, Telecommunications and Digital Economy, Guinea, and the Ministry of ICT, Zimbabwe. Here are some highlights from the week-long convention.
Tune for inclusion and innovation: Days 1–2
On the opening days of WSIS+20 and AI for Good, high-level sessions focused on cybersecurity readiness, inclusive infrastructure, and ethical AI development.
Sessions covered various topics, including Digital Trust and Cybersecurity Readiness, Smart Cities, and Inclusive Infrastructure, as well as Bridging the AI Gap between Africa and the World. The sessions provided valuable insights that national regulators seeking to strengthen institutional approaches to equitable tech governance could draw upon.
The Smart Cities session highlighted innovations responding to local needs. Examples included voice-based emergency alerts in Senegal, designed to reach non-literate populations, and community-driven infrastructure planning in Nairobi.

In AI-related sessions, there were mentions of glaring infrastructure inequalities. With just 1,000 GPUs across Africa vis-a-vis Meta's 250,000 (as highlighted by Dr. Amandeep Singh Gill), calls were made to prioritise African data sovereignty, invest in computer infrastructure, and bridge the capacity gaps.
Policy, access, and gender leadership: Day 3
Panel speakers had an opportunity to bring into sharp focus the national reality as well as the global aspirations:
"We have established over 202 community information centres in rural areas, bringing ICT and government services closer to the elderly and underserved."- H.E. Dr. Hon Tatenda Mavetera, Minister of ICT, Zimbabwe
Key takeaways from Leaders TalkX:

Meanwhile, delegates also graced the invitation-only grand launch of the Network of Women Ministers and Leaders in ICT (NoW) by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). The session convened high-level participants, including H.E. Ms. Rose Pola Pricemou (Minister of Posts, Telecommunications and Digital Economy, Guinea) and Prof. Sandra Maximiano (Chair of ANACOM, Portugal), to drive strategic dialogue on bridging the gender digital divide surrounding emerging technologies.
The NoW platform aims to promote gender-inclusive leadership in ICT governance. The emphasis on capacity building, interregional cooperation, and inclusive policy leadership underscores the importance of ensuring that women's voices and leadership are at the core of digital futures.
Days 4 & 5 Highlights
As WSIS+20 entered the final phase, African voices, many coming from NRAs affiliated with iPRIS, took centre stage during discussions relating to inclusive innovation and strategic regulatory cooperation.
Multistakeholder cooperation and regional vision: Day 4
During a session titled Shaping Africa's ICT Future: The Role of Multi-stakeholder Engagement Beyond WSIS +20 (organised by AfICTA), there was a strong affirmation of the continent's digital ambitions. The session hosted representatives from partner NRAs and sector colleagues, such as Olatokunboh O. (Head of Digital Economy, NCC), who highlighted the importance of community-based networks to bridge the digital divide in Nigeria.
She stated that “We have looked at our community networks, and asked ourselves how do we encourage and drive community-based networks from a bottom-up approach, instead of trying to use a one-size-fits-all.”
Dr. Jamal Tonzua Seidu from the Ghana Cyber Security Agency shared a similar message, highlighting the necessary steps for the future.
 The importance of in-depth research stemming from African Higher Education Institutions and research organisations was highlighted by Prof. Abayomi Jegede, and the need for academia and industry to collaborate with other sectors for practical, wide-scale implementation.
The importance of in-depth research stemming from African Higher Education Institutions and research organisations was highlighted by Prof. Abayomi Jegede, and the need for academia and industry to collaborate with other sectors for practical, wide-scale implementation.
Debora Comparin asked everyone to imagine losing their identification documents and how that would impact their lives. She urged everyone to consider the importance of digital identity. The interoperability of digital identity for multi-sector use paves the way for crucial infrastructure to enable essential services, business interactions, digital cross-border relations, and a multitude of ecosystem solutions.
Wisdom Kwasi Donkor discussed Ghana's digital sovereignty, emphasising the need for accessible, secure, and responsive solutions that cater to the needs of Ghanaians. Local content creation is crucial for Africa's future. A multi-stakeholder model is the key to unlocking this future. African Regional bodies must take the lead in driving the continent's digitalisation.
Kossi AMESSINOU urged the manufacturing of digital infrastructure components and solutions to be based within the continent, especially harnessing the power of solar energy and sustainable energy.
The conversation brought across major themes in the digital space: enable NRAs to build inclusive and responsive sets of regulations; foster peer-to-peer learning across borders; and ground governance in African-led innovation.
Inclusion, innovation, and structural change: Day 5
In the Accelerating Structural Transformation and Industrialization in Developing Countries session, African thinkers revealed ways in which digitalisation may power economic renewal.
Prof. Sama Mbang of the Digital Transformation Alliance (Cameroon) gave instances of how African economies are leapfrogging outdated systems to synchronise industrial policy with frontier ICTs.
Moderator Prof. Adel Ben Youssef (AISMA, University Côte d’Azur) was joined by UNIDO’s Rafik Feki from Senegal, who presented investment and partnership models adapted to the region. The speakers noted that Industry 4.0 can stimulate inclusive growth and fill infrastructure deficits if public-private cooperation is strengthened and human capital development promoted.
A few key points were reinforced during the session: that regulation and innovation must co-evolve; institutional strength is key to resilience and uptake; African voices must be at the forefront of shaping the continent's Industry 4.0 future.
Gender, ageing, and digital equity
In Leveraging ICT for Ageing Populations session, panellists addressed the often-overlooked intersection of ageing, gender, and digital access.
Dr. Asma Brini (Tunisia), Karen Vianey Kenmoe (Cameroon), and other leaders challenged assumptions that the digital economy is only for the young. They called for ethical, inclusive design, where older women and marginalised communities are empowered by, not excluded from, technological change.

Their message presented a compelling argument for intentionally pursuing equity in AI, digital health, and technical education. As African NRAs seek to institute frameworks that work for all their populations, considerations such as age, gender, geography, and income will become vital questions for achieving tangible digital inclusion.
Global stakeholders attended high-level discussions that reflected advocacy for inclusion, rights, ethics, and African leadership in digital transformation.
Reflection was evident upon shared ambitions to close access gaps, defend digital rights, and orient innovation toward the public good. From localised infrastructure planning and gender-inclusive leadership to AI governance and structural digital reform, discussions were clear: Africa is not catching up; Africa is shaping the digital future.
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR).
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
iPRIS was represented by SPIDER in Lillestrøm, Norway, at the Internet Governance Forum (IGF), which took place from 23-27 June. IGF was filled with dynamic interactions and knowledge exchange opportunities for iPRIS, showcasing Africa's strides towards inclusive policy and regulatory innovation. There was also engagement throughout the week from a regular stream of visitors at the SPIDER booth, ranging from regulators, civil society, development partners, and digital rights advocates from around the globe. One-on-one dialogues would be held with the delegates, who would participate in interactive activities such as quizzes and thematic prompts, while also engaging in discussions on the daily regulatory challenges shaping Africa's digital future.
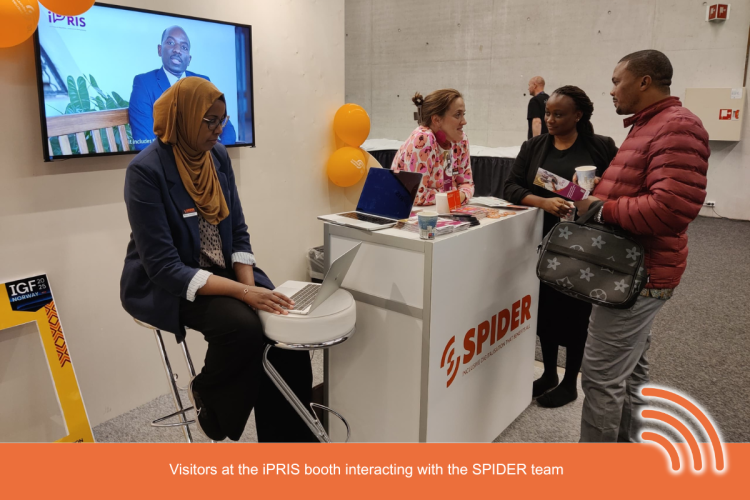

In particular, the iPRIS booth aimed to emphasise regulation that facilitates meaningful connectivity, where "connectivity" is meant to refer to digital access that translates into real opportunities for underserved communities. Visitors to the booth were invited to consider the question: "What does meaningful connectivity mean to you?" This gave rise to some powerful insights emanating from stakeholders drawing from different regions and sectors.
Prof. Abdulkarim Ayopo Oloyede from the University of Ilorin, Nigeria, revealed that “Meaningful connectivity for me as a Nigerian means being able to have access to the internet whenever and wherever. Our challenge remains coverage. I drive to work an hour every morning, half of that time I have no connection, not to the internet nor regular voice calls.”
Additionally, a range of visitors shared video reflections on how digital innovations have truly transformed their work. Among them were health professionals, leaders from community networks, and policy advocates-a testimony to being flexible, inclusive, and rooted regulation.
“We are working with the Communications Authority, which has also set up a regulatory sandbox to explore new ways in which spectrum that is available can also be provided to community connectivity organizations to make sure that no one is left behind in the current digital age,” said Barack Otieno, Chair of the Association of Community Networks in Kenya, highlighting how regulatory reforms are enabling connectivity for underserved communities through new licensing frameworks and innovative spectrum use.
IGF 2025 provided a timely opportunity for iPRIS to contribute to broader global conversations on internet governance, spectrum policy, AI regulation, and regional cooperation. When the conference finally ended, the iPRIS team expressed their appreciation to all the people who visited the booth, shared their experiences, and raised the profile of African regulatory leadership on the world stage.
Keep an eye on our LinkedIn page for all the recent updates, interviews, and lessons from the iPRIS Project.
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR).
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
After an intense year of collaboration, peer-to-peer learning, and policy innovation and a successful, insightful, and engaging Regional follow-up phase in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, in October 2024, the iPRIS 2024A cohort officially joined the iPRIS alumni community. The cohort’s wrap-up plenary brought together national regulatory authorities from The Gambia (PURA), South Africa (ICASA), Lesotho (LCA), Uganda (UCC), Mauritius (ICTA), Tanzania (TCRA), regional bodies such as CRASA, the SPIDER team, PTS representatives, and a network of peers and experts.
The plenary session opened with acknowledgements from the facilitator, Kerstin Borglin, SPIDER, of the members present, including Katrina Schyberg, the project lead of iPRIS at PTS, Lars-Göran Hansson and Gustav Lenninger from PTS, and the other SPIDER associates in Stockholm: Caroline Wamala, Ulf Larsson, Alexandra Högberg, Katja Sarajeva, and Edna Soomre. The session was reflective and committed to showcasing achievements and the importance of continuous peer learning, all while highlighting the programme's core themes.
Showcasing Change Initiatives
Participants from respective countries presented the outcomes of its Change Initiatives (CI), reflecting on lessons learnt and shared plans for future implementations.
In the earlier session, South Africa’s ICASA shared its experience in developing Dynamic Spectrum Access (DSA) regulations. The project accomplished technical assessments and legal evaluation with ongoing public hearings. A few challenges were encountered, including resource constraints and timeline overruns; however, effective stakeholder engagement and diverse regional perspectives helped mitigate risk.
Lesotho’s LCA followed and shared the LCA’s cybersecurity regulatory instructions, which were approved in March 2025. They also highlighted the five-year alignment of the biannual reporting plan with stakeholders. Uganda’s UCC presented a revised National Numbering plan, and authorisation frameworks were in the final approval stages. The project focused on internal workflows through restructuring and leveraging data-driven management practices.
Mauritius’s ICTA discussed their public dashboards in development and also presented its updated Quality of Service (QoS) evaluation framework, which integrates crowdsourced user data and engages operators. The Gambia’s PURA introduced new consumer complaint-handling guidelines with refined KPIs. And Tanzania’s TCRA introduced its draft guidelines for satellite-terrestrial spectrum sharing. Established with stakeholder input, their project fosters partnerships between Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) and satellite operators.
Peer and Expert Reflections
The representatives from PTS, SPIDER, and CRASA applauded the cohort’s project presentations for their comprehensiveness, intent, and regional relevance. Emphasis on the importance of real-time monitoring and stakeholder engagements. Participants were also encouraged to view the conclusion of their CIs as the beginning of a continuous institutional development process. The participant countries highlighted the advantage of peer networks for sustaining change.
Looking Ahead
The 2024A cohort demonstrated that impactful regulation is possible when local expertise is combined with structured peer learning. The plenary session concluded with a unified understanding that real change requires sustained effort, and iPRIS provides a platform to facilitate evidence-based digital regulation across Africa.
Here are some video highlights from the cohort:
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR).
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
In Juba, South Sudan, the 1st Advisory Council and 30th General Assemblies under EACO were launched, with over 250 regional stakeholders convened under the theme, "Shaping the Future of the East African Region through Digital Transformation." The high-level event on 9-13 June 2025 was hosted by the National Communication Authority (NCA).
This landmark congregating marks a significant milestone for EACO, as it signals the inauguration of the Advisory Council meeting-a forum consisting of Members and Partners that meet once every two years to adopt and coordinate recommendations from the different Assemblies. Together with the Advisory Council, the four annual Assemblies of EACO-i.e., Regulators, Postal Operators, Telecommunications Operators, and Broadcasting Operators-have also convened in Juba for discussions concerning the regional ICT landscape.

Digital transformation and inclusive growth in focus

Day 1 focused on digital transformation as a critical dimension towards unlocking East African socio-economic development potential. Loads of thematic sessions were debated, including the following topics:

South Sudan hosting the Assemblies enhances NCA's regional leadership in telecommunications matters and projects to establish a digital hub.
"When we deliberate over the coming days, let us remain aware that the policies, recommendations, and standards we adopt here will ultimately touch many lives," stated Mr Gieth Mathiang Kon, Director General of NCA, during the opening day.
Regional leaders join forces to frame ICT policy
Day Two was marked by the official inauguration of the General Assemblies, drawing together regulatory and operational stakeholders from across East Africa. The arrival of Hon. Dr. Chris Baryomunsi, Minister of ICT and National Guidance from Uganda was warmly welcomed by top officials from the host country. The participation of such senior policymakers surely demonstrates a shared commitment to the region harmonising its ICT policy and regulatory framework with regional priorities and the African Union’s digital transformation agenda.
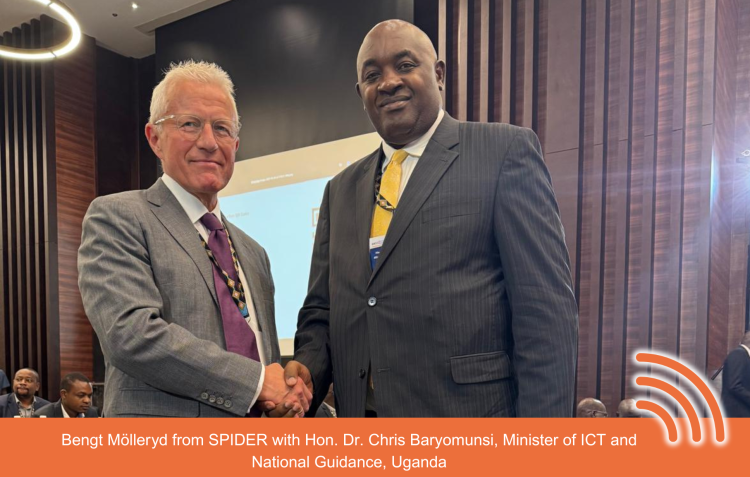

Marking a new chapter in regional ICT leadership
Reflecting the successful conclusion of the 1st Advisory Council meetings, the National Communication Authority announced that the 1st Advisory Council meetings had come to a close after being held from 11 to 13 June 2025 in Juba.
The final day was characterised by a comprehensive report from the outgoing Chair of EACO, Dr. Samuel Muhizi of Burundi, offering key reflections on the organisation's progress and its strategic priorities. However, a significant moment in the proceedings saw the official handover of the EACO chairmanship from Dr. Muhizi to Mr. Gieth Kon Mathiang, Director-General of the NCA, South Sudan.
In their final moments, the meetings adopted a Final Communiqué that encapsulated crucial resolutions and undertakings from member states aimed at enhancing collaboration and expediting digital transformation across East Africa.
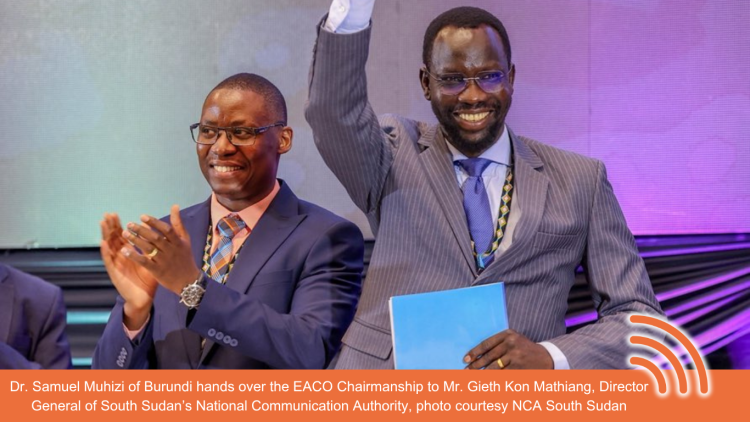

The interface for collaboration and regional integration
EACO remains firmly positioned in coordinating the regional space for inclusive and sustainable growth through digital transformation. These instruments- the Advisory Council and General Assembly- pave the way for peer learning, policy alignment, and institutional collaboration enhancement among the telecommunications sector of East Africa.
As a participant in iPRIS, EACO plays a pivotal role in assisting national national regulatory authorities (NRAs) as they strive to implement their change initiatives in their respective countries.
For more updates from the EACO 1st Advisory Council and 30th General Assemblies, follow the official proceedings here
For more information on the role of Regional Regulatory Organisations (RROs) like EACO in iPRIS, click here
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR).
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
The National Communications Authority (NCA) of Ghana hosted a high-level delegation from the Independent Communications Authority of South Africa (ICASA) from 28 to 30 May 2025 in Accra. This is a strategic exchange that showcases the building blocks behind regional collaboration among National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs) and the shared commitment to universal access on the continent.
The visit, with a focal point on Ghana's implementation of universal access concepts, further reinforces a strong bilateral relationship between the country and South Africa. ICASA's visit to Ghana was aimed at learning from the country's holistic, multi-stakeholder approach to developing broadband infrastructure in rural and underserved communities through the NCA.
Rev. Ing. Edmund Y. Fianko, Acting Director General of NCA, reaffirmed that West-South cooperation remains of immense value in innovative regulation. Additionally, he stated that Ghana's success factors reside in sustainable financing mechanisms and inter-agency collaboration. The Ghana Investment Fund for Electronic Communications (GIFEC) is one of the critical pillars of Ghana's strategy and is funded through a 1% contribution from the revenues of licensed operators. This model has facilitated the rollout of 2G and 3G mobile infrastructure services in underserved areas, thereby promoting digital inclusion and greater access to voice and data services.
According to ICASA Board Member Councillor Cathrine Mushi, the visit was crucial for South Africa's Vision 2030, which aims for universal access to broadband. She acknowledged that South Africa faces structural challenges—legal and regulatory fragmentation being the primary concern—and expressed interest in Ghana's enabling frameworks and implementation options.
The other delegate at the visit was Mr Eric Nkopodi, Senior Manager of Engineering and Technology at ICASA, who emphasised that South Africa continues to focus on refining deployment frameworks, rights-of-way, dispute resolution, and rural infrastructure assessments. Coordinated institutional efforts being undertaken in Ghana provide practical insights to South Africa on its ongoing regulatory reforms.
During the three-day visit, the ICASA delegation met with key stakeholders, including GIFEC, American Tower Company, West Africa Cable System (WACS), and local government representatives, who provided a well-rounded view of the technical and policy environment underpinning Ghana's progress towards digital inclusion.
Not only does this benchmarking visit lend weight to the ongoing need for peer learning, but it also demonstrates how universal access can be accelerated through inter-agency coordination, sustainable funding, and regional knowledge exchange. This serves as a reminder that Africa-led solutions remain pivotal in setting the technological course for the continent.
The Europe Phase of the fifth iPRIS cohort (2025B) officially concluded in Stockholm on 21 May 2025, marking a critical milestone in the iPRIS peer-learning journey. Over a two-and-a-half-week period, regulatory ICT experts from six African National Regulatory Authorities (NRAs)—Eswatini (ESCCOM), Sierra Leone (NatCA), Nigeria (NCC), Tanzania (TCRA), Uganda (UCC), and Zambia (ZICTA)—collaborated alongside representatives from Regional Regulatory Organisations - RROs (WATRA | L'ARTAO, EACO, and CRASA) and their European counterparts.
The cohort underwent rigorous peer learning aimed at reinforcing regulatory frameworks, supporting inclusive digital governance, and correlating national ICT strategies with international standards while preserving in-country relevance.
Week 1 highlights: Transforming policy through insight and peer learning
The opening week of the programme laid the ground by way of strategic dialogue and institutional exchange. NRAs presented their Change Initiative. The Change Initiatives are conceived as vehicles for system-level change to bridge the digital divide in Sub-Saharan Africa.
The discussions during the first week also underscored Sweden’s regulatory shift to broadband and mobile termination, aligning with the EU’s broader legislative frameworks. The rise of digital services like WhatsApp continues to disrupt traditional telecom markets, as discussed by Fred Capper from the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS).
Katarina Schyberg (PTS) moderated day 2 sessions with an introduction to the iPRIS Learning Management System by Petra Rindby from SPIDER. The cohort then explored the Swedish regulatory context in depth through:
Our 3rd day kicked off with Andreas Wigren from PTS unpacking Sweden’s broadband strategy—highlighting how a market-driven approach, supported by strategic public investment, has shaped nationwide connectivity. Jens Ingman followed with insights into Sweden’s broadband mapping project, which has collected geospatial data annually since 2007 to support evidence-based policy.
In the final session, spectrum management took centre stage. Amela Hatibovic Sehic, Gustav Lenninger, and Fredrik Johansson of PTS shared Sweden’s approach to frequency planning, auctions, and international coordination—emphasising societal value over revenue.
On Day 4, AnnaLena Sandberg and Lisa Ljungqvist led sessions on end-user protection and digital inclusion through the lens of the Swedish Electronic Communications Act. This was followed by detailed discussions on numbering and addressing by Claes Hultholm and Jesper Simons.
Day 5 began with a focus on secure communications and cybersecurity, led by Per-Erik Vitasp, Gustav Söderlind, and Joakim Aspengren. They outlined Sweden’s regulatory requirements around availability, integrity, confidentiality, and privacy in telecoms.
In session two, Peter Thörnqvist guided a discussion on future-facing regulatory challenges. The day closed with Part 1 of a Project Management session by Malena Liedholm Ndounou from SPIDER, before the group headed out to explore Stockholm on the iconic Ocean Bus.
Week 2 highlights: Building collective capacity for inclusive connectivity
In the second week, regional and cross-continental cooperation further intensified through ideation circles, peer-to-peer presentations, and immersive site visits, including engagements with Ericsson and STOKAB, thereby providing the participants with hands-on insights into telecom infrastructure and data-driven policy design.
Day 1 started with thought-provoking discussions moderated by Katarina Schyberg from PTS. Astrid Olofsson and Björn Backgård led the first session on competition regulation in the telecommunication market, highlighting the importance of economic regulation to prevent monopolies and promote innovation. The session also provided insight into the four-step methodology for regulated markets and the three-criteria test that assesses barriers to entry, market trends and competition law sufficiency.
The second part of the day was held at SPIDER HQ in Stockholm University, and the first session, "Beyond Universal Access", was led by Caroline Wamala Larsson and Malena Liedholm-Ndounou from SPIDER, which challenged them to reimagine access as more than just connectivity. The role of diversity, equity and inclusion in achieving inclusive connectivity was also highlighted.
The other "Beyond Universal Access" sessions discussed challenges in Sub-Saharan Africa's mobile access, highlighting a 61% usage gap and emphasising the need for gender-responsive policies and digital literacy programs to address these gaps.
Day 2 sessions were peer-learning circles where African and European counterparts hold discussions together. The perspectives from the experts and team-based ideation drove dynamic participation, proving that when leaders learn together, systems change simultaneously. WATRA | L'ARTAO, CRASA, and EACO, also gave an update, reinforcing the critical role of regional structure in shaping Africa's digital culture.
Day 3 began with a full day of Industry learning experience at Ericsson, exposing participants to advanced telecom technology and real-world infrastructure, detailing insights into emerging digital infrastructure forms.
Day 4 was focused on MEAL (Monitoring, Evaluation, Accountability, and Learning), with Katja Sarajeva from SPIDER underscoring the importance of evaluation frameworks in digital policy interventions. Thereafter, the final modules of Project Management took place, and Kerstin Borglin and Malena Liedholm Ndounou guided participants in drawing up implementation plans. The day ended with a networking cruise around the Stockholm archipelago, allowing participants to reset after the intensive sessions and interact with peers in the sector.
The rest of the day today was dedicated to part two of "Beyond Universal Access" with Caroline Wamala Larsson and Malena Liedholm Ndounou from SPIDER and covered inclusive access strategies beyond just connectivity, with a focus on gender-responsive policy and digital literacy initiatives. The day ended with a study visit to Stokab, where the participants acquired hands-on exposure to Stockholm’s public fiber infrastructure.
Week 3 highlights: From vision to action
The closing week of this convening centered around strategic project planning and readiness for implementation. Key highlights from Day 1 and 2 included:
The cohort ended with each team discussing their Change Initiative project plans in an extensive and highly insightful 'Way Forward' session, setting the stage for measurable transformation leading into the Africa regional phase later this year. The outputs from this phase now feed into the next phase of the iPRIS cycle: the Africa Regional Phase (6-9 October in Botswana), where the peer learning continues in contextualised form and Change Initiatives edge closer to operational implementation.
Watch the video highlights from Sweden below
Here are some photo highlights from Sweden
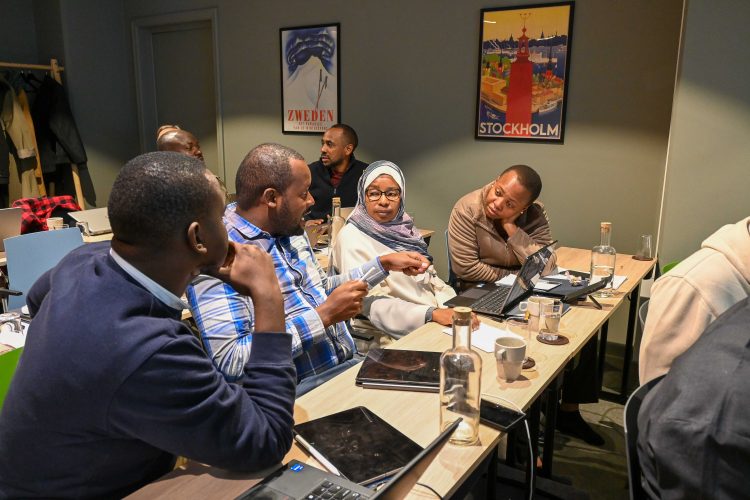

Peer-to-peer discussions during the round among African and European counterparts
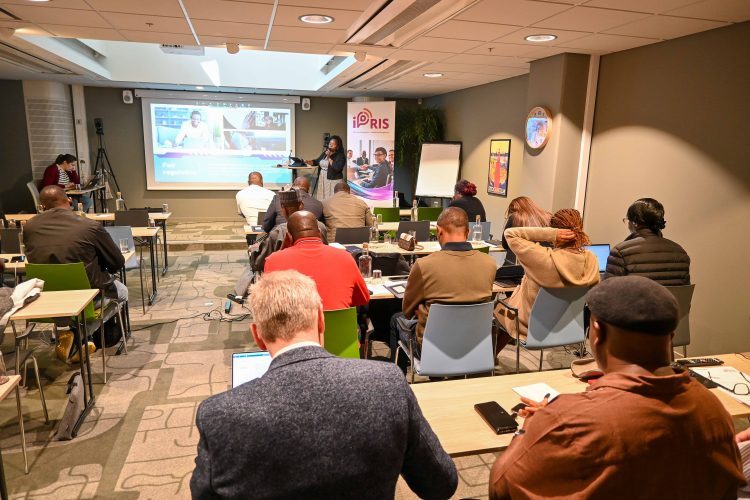

iPRIS participants follow discussions from peer experts during the round
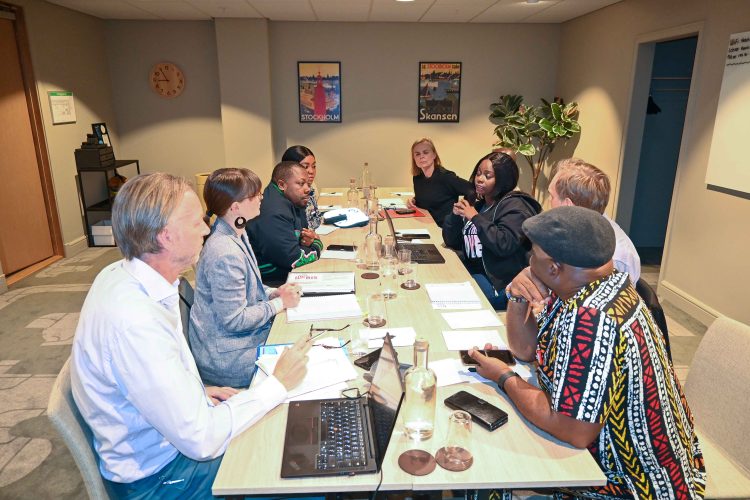

Peer-to-peer discussions during the round among African and European counterparts
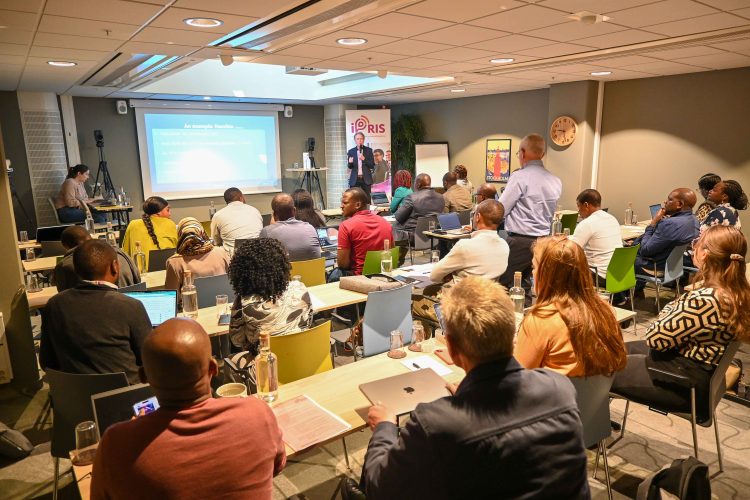

iPRIS participants follow discussions from peer experts during the round
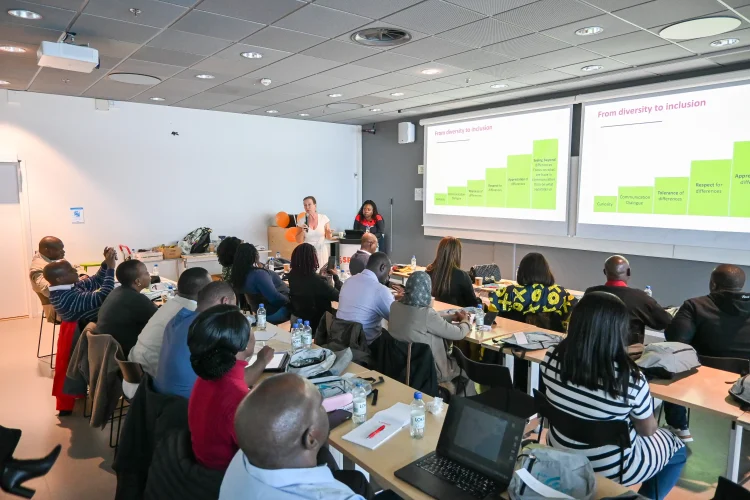

"Beyond Universal Access" presentation with Caroline Wamala Larsson and Malena Liedholm Ndounou from SPIDER
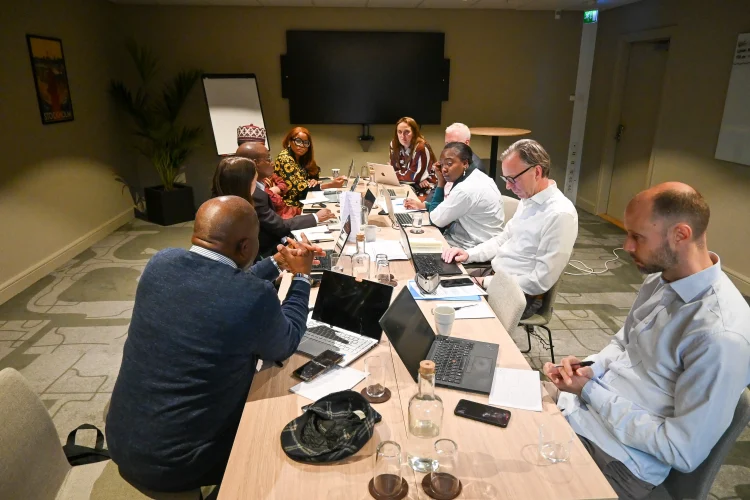

Peer-to-peer discussions during the round among African and European counterparts
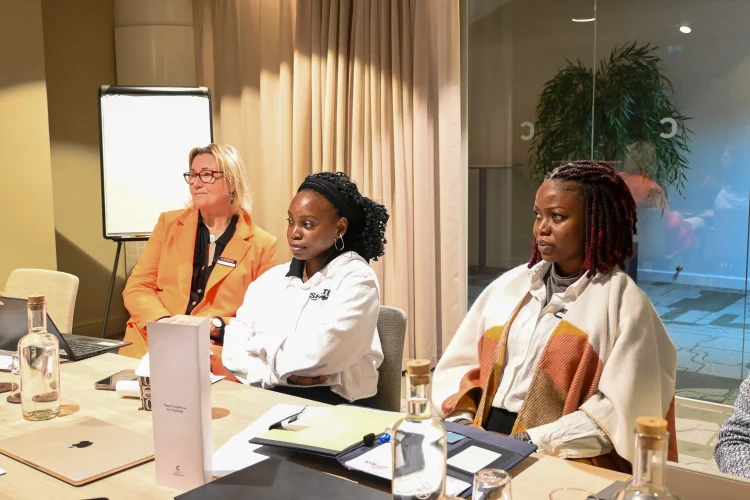

Peer-to-peer discussions during the round among African and European counterparts
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR).
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).
Borgarfjordsgatan 12, Kista,SWEDEN
Postal Address: Stockholm University, Department of Computer and Systems Sciences/DSV, SPIDER, P.O Box 1073, SE-164 25 Kista, Sweden
Copyright © 2025 iPRIS. All rights reserved.