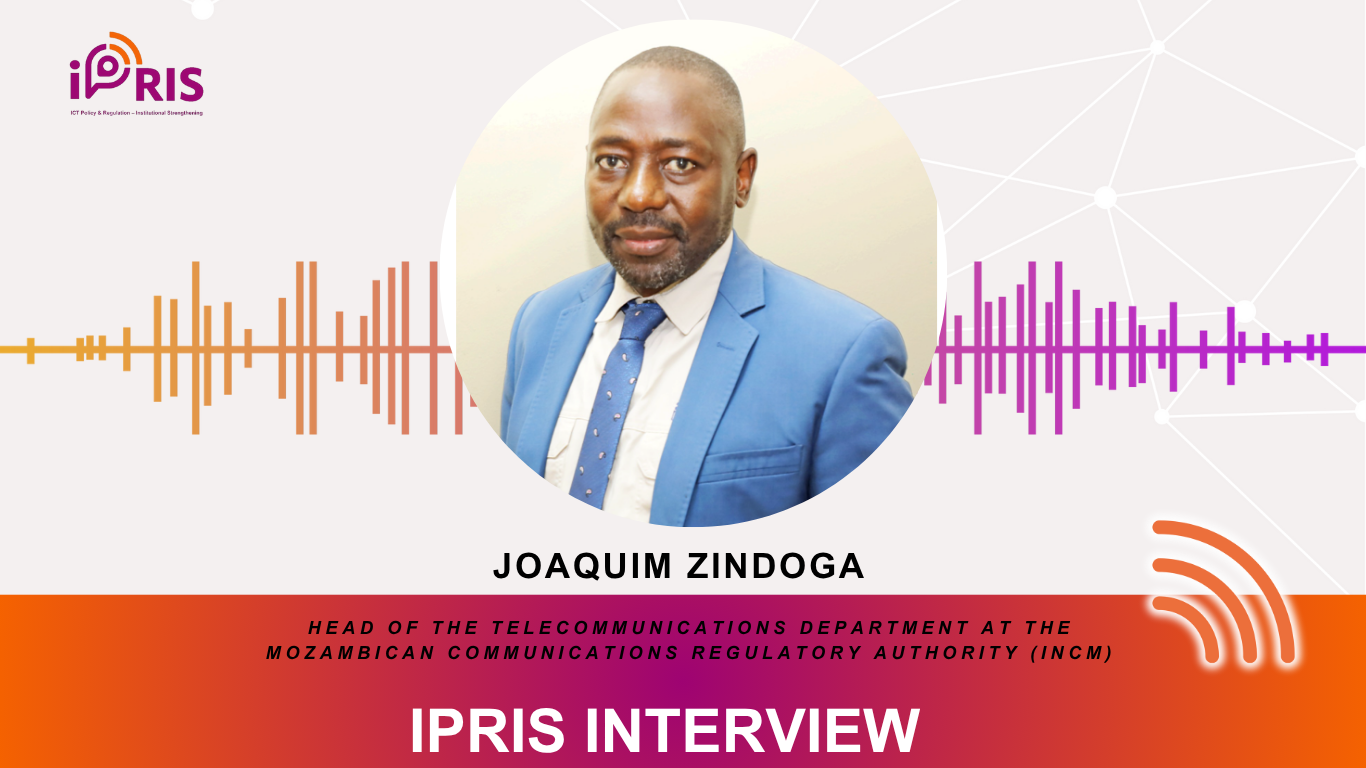
Mozambique’s telecommunications sector is undergoing a regulatory transformation, with national roaming emerging as a key lever for expanding connectivity, promoting infrastructure efficiency, and driving rural inclusion. At the forefront of this shift is Joaquim Simão Zindoga, Head of the Telecommunications Department at the Mozambican Communications Regulatory Authority(INCM). With 24 years of experience in the ICT sector, including 14 years at the National Telecommunications Company (TDM) and a decade at INCM, Zindoga brings deep technical and policy insight to one of Mozambique’s most ambitious regulatory reforms to date.
In this conversation, he reflects on Mozambique’s newly gazetted national roaming regulation, its social and economic rationale, its potential to close access gaps in commercially unattractive areas, and its grounding as a change initiative shaped by the 2018B cohort of the International Training Programme (ITP), a predecessor to iPRIS. Zindoga shares lessons learned, regional inspirations, and the regulatory strategy that transformed the idea from a workshop to a law.
This interview has been edited for clarity.
iPRIS: Could you briefly introduce yourself, INCM, and its core regulatory responsibilities
Joaquim: I have been the head of the telecommunication department since 2021. INCM is the national regulator for communication and postal services. It was founded in 1992 when the former TDM, the incumbent, decided to separate dispatch management and the core service from the operator. Since then, they have grown significantly, particularly in adopting best practices for regulatory compliance. We made some advancements after reviewing the National Law of Telecommunication. We introduced the postal law and consumer protection, as well as quality of service, after 2014. This indicates some progress in terms of regulation.
The institution is financially independent, but its political independence is less pronounced. You know that the person who nominates the CEO of the regulator is the minister, who the President appoints through the Minister of Communication. So we can't say that we are fully independent. We remain linked to the government, but financially, we are independent. Our operations are based on resources from telecom fees (annual spectrum use fees) and other income sources. However, we do not receive funding from government officials. We are almost 150, with representations across the country, except in the capital, where we are based. The head office is in Maputo, and we don't have representation in the other two provinces in the central and southern parts of Mozambique.
iPRIS: Over the past three years, INCM has achieved several regulatory milestones, including the recent decree. What would you highlight as key achievements during this period, and how does this regulation fit within that broader progress?
Joaquim: Well, I can start from the roaming decree that has been announced, and last week, we also announced the proposal for how we are going to implement the national roaming. Before national roaming, we introduced a new decree requiring customer and ICT equipment registration. This meant that all customers and their related ICT gadgets had to register. That is a new law. That is quite a good one. We also have the review of the quality of service indicators, based on the ITU's recommendations and consumer protection. The other decree was dispute management, which is related to customers and providers.
Our approach to managing this aligns well with the recent decrees promulgated in the country, as it addresses the issue of uncovered areas, particularly those served by only one provider. Given our efforts to maintain communication continuity, we enforce it. It was taken from the initiative of the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS), and it was well received. The government is pleased with our resolution and looks forward to seeing how it will be enforced, as it's expected to alter the market landscape significantly.
Normally, our setup is that everywhere we have communication, we have three antennas, or we have three cables in the poles, meaning each operator has their own infrastructure. However, there are areas where none of these infrastructures are present. If they were to use roaming, they could deploy one or two of these infrastructures in other locations, ensuring the country remains connected. Instead of keeping some areas where they think, or they might think that is the only way they can have more revenue from those areas. It fits very well because it is a continuation of the infrastructure sharing decree, which says that either passive infrastructure or active infrastructure can be shared. Now, with roaming, we are looking at active infrastructure, which aims to reduce the investment required for new areas that are not covered, or for better coverage in areas where they are currently.
iPRIS: You participated in the ITP programme in 2018. What were your biggest takeaways from that experience, and how did it influence your approach to regulatory development or institutional change?
Joaquim: The first takeaway was the way that the PTS approached the market, especially our issue. And we had many ideas. We were three in our team looking at the roaming. We were just throwing ideas around in the hall. PTS was directing our ideas on how we should think about it. Initially, normal roaming wouldn't change much, and the investment landscape in the country wouldn't shift significantly. Others were saying no, but people might not want to use another network because we have the capacity of a phone with two SIM cards, and with all three SIM cards, we can do whatever we want.
However, the initiative's direction shifted to an investment issue, focusing on investment savings and the amount of money that investors will save (the Cost of operator and CapEx costs). This meant that instead of maintaining three Base Transceiver Stations (BTS) in one place, we now have only one. It means that our cost will reduce by at least 1/3, and together, we will have just the responsibility of keeping one BTS alive. The rest of us will be using the same via roaming. It means we reduce the amount of petrol and electricity used, as well as the security needed for all sites.
So it's a huge saving method by all means, and that direction from PTS was the key for us to make the initiative a novelty in our market. Everyone views framing as infrastructure sharing, but not as a means to save money for the operator, allowing them to reinvest the savings in other areas and generate additional income. So, that was our main takeaway: being in an environment where ideas are allocated in a certain way, and they flow fluently. It allowed us to think differently. And when we came back, it was like, yeah, good idea. Because before we left, we had to submit proposals. I recall submitting my proposal to my boss, who asked, "What are you going to do in roaming?" No one wants to use roaming because it doesn't offer the perspective of being a way to save money for the operators. However, from ITP, we gathered information and different ideas, which brought out the whole body of roaming.
iPRIS: In the Roaming Decree approved this May, INCM commits to expanding mobile access in commercially unattractive and rural zones. What specific market challenges or user needs triggered this regulatory push, and how did the Change Initiative help shape this intervention from 2018 to now?
Joaquim: Many things have changed. However, we remain with the same challenge. Most people in rural areas no longer use phones for calls; instead, they rely on them as their primary means of communication. I recall a place where we visited, and the only provider was one of the companies; most of the population in that area used the financial platform from another operator. For instance, someone has to travel about 10 kilometres to find their network so that they can receive the money from whoever is sending it, withdraw the money, and then buy whatever they want before coming back. But now with roaming, they don't need to move away from home for 10 kilometres to find my network, because they will be using the service from another network, but still with their original service provider.
This is one of the gains that this resolution will bring to those areas where the risks and the expense that they have to incur are elevated due to the lack of coverage. While some receive their salary through a mobile money wallet, they must withdraw money and travel to do so. So, you have to pay for transport to get your money or to check if you have a message with the amount waiting to be received. So, the money is here; you have paid this amount of cash for transport, and then you withdraw your money and come back. So all those inconveniences will be eliminated.
The other thing is the flooding and emergency communications. It also serves as a helper, as some of the infrastructure lacks sufficient strength to withstand natural disasters. And when there is a cut of one network, we can use another network as a provider via roaming, because now we have roaming; before, we didn't have it, and they could wait for weeks until their network was available, or they had to buy a new SIM card for that network that is alive. However, buying that one is impossible now, due to the floods; you cannot move away from your village to the next area where it is available. It is a social decision aimed at helping our people, particularly in rural areas where they have only one network operating. They are currently forced to use a network that is not their preference due to limited coverage options. Now, they will have the ability to choose which network they prefer to use via roaming.
iPRIS: The Decree outlines technical and commercial frameworks to ensure fair and transparent roaming agreements. What lessons from your ITP experience were most useful in designing or advocating for these structural provisions within Mozambique’s regulatory ecosystem?
Joaquim: After we came back in 2018, we started a trial. And this trial allowed us to draw some lessons. The main lesson from this was that we have different infrastructure, which was used as an excuse to claim that I couldn't connect to the network because our infrastructure wasn't compatible. But then we ask them, when I go to Switzerland, do they know that my technology here in Mozambique is this one, so that they can buy it to allow my network to operate? They said, No. So, how are they operating? So this is when we discovered that that was an excuse. So we formed the law. We also mentioned that this is mandatory, so ensure your network allows hosting another network's customer. We're unsure what you'll do next, whether you'll invest or change the software. Regardless, do what needs to be done. With international roaming, we could easily say that, no matter what, we could go back and ask, "How do you handle an international traveller joining your network? How do you charge him?” They provided us with answers. So we tried to do the same with our national roaming to see what would happen.
We started conducting trials and encountered issues with SMS and data. However, the voice calls performed well, suggesting that the operators didn't want to provide roaming data. They just wanted to roam the voice and SMS. SMS is beneficial because it enables USSD services for financial services, as we've emphasised the importance of using wallets everywhere. They facilitated us easily, but now that data is their cash cow, they were very difficult to open, but we finally got it. With the use of Call Data Records (CDRs), it is possible to receive or interchange between them, to say, look, this is the CDR that I received from this customer, let’s call him John. John was hosted on my network and spent a specific amount of time using it. This is the bill they need to pass to you.
iPRIS: One of the stated goals of the new regulation is to support the entry of new market players who lack infrastructure. Could you speak to how this aligns with regional trends in spectrum and infrastructure sharing, particularly within CRASA or SADC contexts?
Joaquim: Within CRASA, we gained the best experience from South Africa. They had more than three operators using roaming, smaller ones, which the big operators eventually acquired. However, it was a start-up from small operators, especially in areas where they believed there were few efficient areas to cover. We drew on that experience, as well as the Angolan experience, where they were the first to consider roaming, although they have not yet implemented it. This might also be due to political reasons, and issues related to politics can sometimes push you away from what you initially planned.
We believe that if the operator fully allows national roaming, they will have a chance to expand their new services through new entrants, who can say, "I want this area, do the service," and then see the outcome. Once that is done, they can buy into that project and cover it normally with their infrastructure. For the new entrant, it is not only about attracting new investors but also about entering new areas that have not been covered before. So, if they apply roaming, instead of being alone, they will be with several operators. They can invest and see how much they will cover in a specific area.
From the perspective of a new entrant, the market is wide open and offers effective investment opportunities. If we say that, and it is also an experiment, they can embark on it to see what happens in the end. We don't have any data beyond South Africa and Angola, but the South Africa experience is well-known, and it involves three companies that were acquired. But first, they started via roaming.
iPRIS: Developing a national regulation from a change initiative is rare and commendable. What institutional or political factors enabled sustained progress over several years? And what advice would you give to another NRA facing delays in pushing similar initiatives?
Joaquim: The only institution that must do all is the regulator, the NRA. The NRA needs to push, especially with the incumbent ministry, such as the Communication Ministry, and explain to them why. We've had three years of back-and-forth discussions, as they've wanted to understand the rationale behind roaming. How are we going to do this? What is this? How much are we going to charge? All those questions, but with the NRA, we knew what we were looking for. We could convince the political side that this was what we wanted, and we showed them with numbers, especially when we approached them to say that communication is a right for everyone.
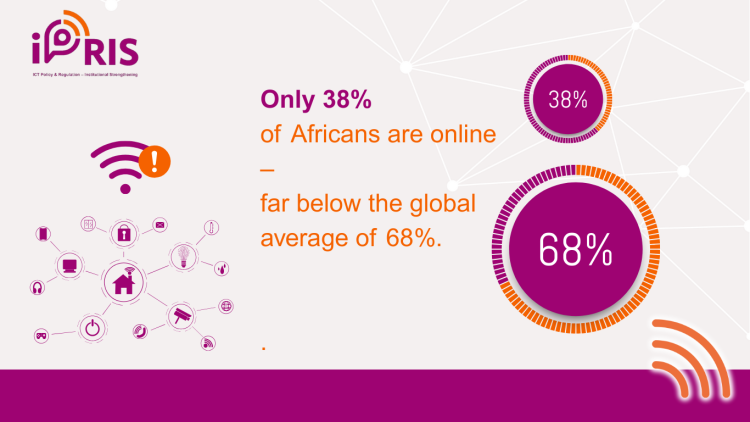
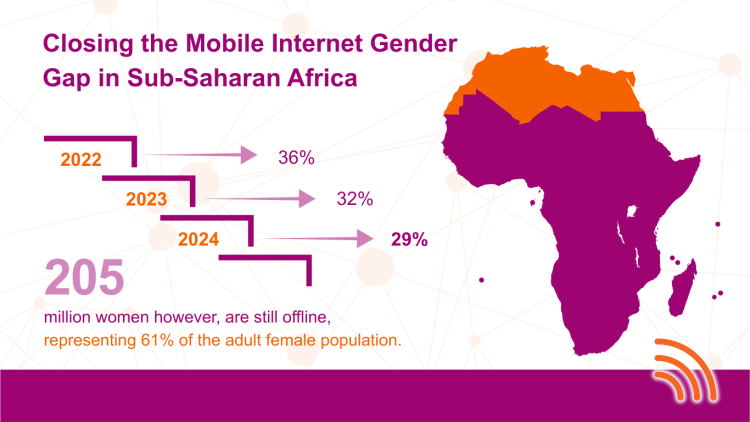
But we have more than 20% of people who are living in areas without coverage. Do you want to remain in this situation or not? So that changed their perspective, because they saw it from a political standpoint. So, they started using our roaming as a flag, saying, "No, don't worry, we will bring communication here via roaming." Roaming will work like this. We'll have all the services that you want. So that was the way that we got them. We brought them in, and they supported us. Even in the last week, when we had the meeting with the board, the CEO was asked about roaming. And the Minister of Justice, who signed the document, asked, ‘You told me to sign this document very rapidly. Where is the roaming? Because I was in a certain place which did not have the service.’ She told him that no political issue is solved now, explaining that we were dealing with the technical aspects, which take some time, as we test various things until it comes alive.
But for all to happen, we needed the document to be signed first. They wanted to know when the roaming will be active. They added that they want to use just one number, knowing that wherever they go in Mozambique, they can call home, receive calls, and use data from their phone. Politically, the national regulator must reach out to all relevant parties. They explain the document's content, their objectives, and the benefits of implementing the initiative. So that's how we got it.
iPRIS: Now that the regulation has been gazetted, what mechanisms does INCM have in place to monitor impact and encourage operator compliance? And is there a scope for regional benchmarking or harmonisation across Lusophone countries or RROs?
Joaquim: CRASA has a regional organisation for roaming, and we are aiming to harmonise everything that's happening in one country. In April, we had a meeting in Lesotho, and we had a panel discussion where we exposed the issue. If, for example, Kenya has done something successfully, why am I competing with Kenya instead of cooperating with them and asking Kenya, How did you get to this point very quickly? So we harmonise, we don't compete. The idea, even among SADC countries, is to cooperate in a way that shares all successful experiences. We copy them, bring the expertise, and they provide us with ways forward for our regulation. Upon checking, they're mostly similar due to the harmonisation under the SADC and CRASA, where we are working to achieve harmonisation.
We are currently discussing this because not all countries offer national roaming. We're interested in regional roaming that feels like being at home, without the high charges. Imagine that in some countries, one megabyte costs more than $10, making it very expensive. The harmonisation addresses these issues, particularly the roaming charges in the region. The benchmarking has been COMESA and the Eastern Region Association, which has implemented regional roaming. This gives us the strength to make it in SADC and potentially in other countries. When they see that our national roaming is working, they might come to us and ask how we did it, and we are open to helping them.
In the ITP program, we had Zambia, Namibia, Botswana, among others, and they still remember the roaming project from our side. I remember the Zambian project was on e-waste. If we start with the regulation from our side regarding e-waste, I know where to look for information on how they successfully implement the decree. When they decide to implement national roaming, they will recall that in 2018, a team from Mozambique initiated the idea, and the roaming is currently operational. So that's the status among Lusophone countries.
When we came back from Sweden, I was involved in a project aimed at implementing roaming between the Lusophone countries. But I don't know what happened, because we never spoke about it again. Priorities were roaming in Brazil and Portugal, which were the two most visited countries by other countries. So we're expecting to have at least a special price from those areas. However, upon consulting the operators, we found that their tariff, particularly for calls between Portugal and Mozambique, is the most affordable international call tariff. So, it is already on discount because most Mozambicans travel to Portugal, and the goal is to prevent them from switching their numbers by encouraging them to continue using the national number. We have not yet received any news regarding Lusophone roaming, but there is a development that suggests the possibility of roaming in Lusophone countries.
iPRIS is coordinated and implemented by SPIDER in strategic and technical partnership with the Swedish Post and Telecom Authority (PTS) and the Luxembourg Regulatory Institute (ILR).
iPRIS is funded by the European Union, Sweden, and Luxembourg as part of the Team Europe Initiative “D4D for Digital Economy and Society in Sub-Saharan Africa” (Code: 001).